Table of Contents
Quality Service Guarantee Or Painting Free

Get a rental agreement with doorstep delivery

Find the BEST deals and get unbelievable DISCOUNTS directly from builders!

5-Star rated painters, premium paints and services at the BEST PRICES!
Loved what you read? Share it with others!
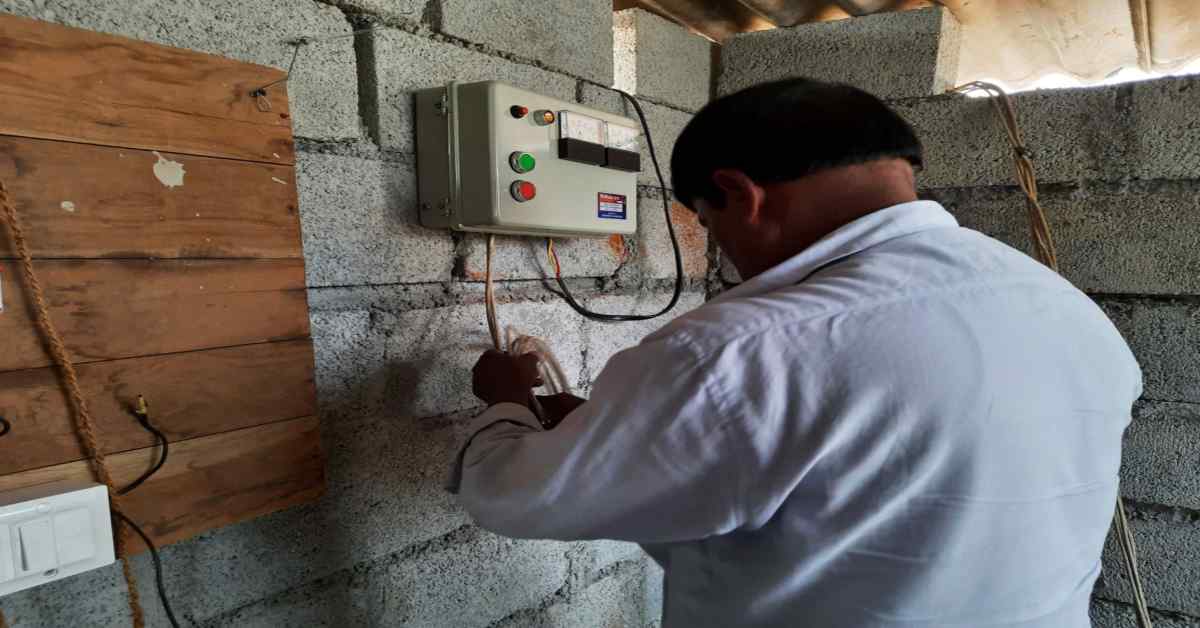

House Fuses: Safeguarding Your Home's Electrical System
Table of Contents
With the increasing reliance on electrical appliances in Indian homes, understanding house fuses has become more important than ever. This guide offers homeowners essential insights for safely managing their electrical systems. From identifying a blown fuse to considering an upgrade, it provides a thorough look at maintaining and enhancing home electrical safety.
What is a Fuse?
A fuse is like a tiny guard in electrical systems. It has a metal wire in a protective case. Its main job is to keep electrical circuits safe. If too much electric current tries to pass through, the metal wire gets hot and melts. This melting stops the flow of electricity, protecting against overheating and possible fires. In short, a fuse helps prevent electrical problems by breaking the circuit when there's too much current.
Fuses in Household Electrical Safety
In older Indian homes, fuses are a common sight. They work silently behind the scenes, ensuring that any electrical overload is quickly managed by breaking the circuit. This simple yet effective mechanism prevents damage to appliances and reduces the risk of electrical fires.
Quality Service Guarantee Or Painting Free

Get a rental agreement with doorstep delivery

Find the BEST deals and get unbelievable DISCOUNTS directly from builders!

5-Star rated painters, premium paints and services at the BEST PRICES!
Fuses vs. Modern Circuit Breakers
While fuses are effective, they have limitations compared to modern circuit breakers, especially in the context of convenience and usability:
- Fuses need to be replaced after they blow. This requires identifying the blown fuse and physically changing it, which can be a hassle and sometimes dangerous if not done correctly.
- Circuit Breakers, on the other hand, simply need to be reset when they trip. This makes them more user-friendly and a preferred choice in newer Indian homes and renovations.
| Feature | Fuses | Modern Circuit Breakers |
| Function | Melts to break the circuit in case of excess current. | Trips to break the circuit in case of excess current. |
| Resetting | Typically one-time use; needs replacement after melting. | Can be reset manually after tripping, no need for replacement. |
| Response Time | Reacts relatively slower to overcurrent conditions. | Responds quickly to overcurrent, providing faster protection. |
| Protection | Offers basic protection against overcurrent and short circuits. | Provides advanced protection, including features like ground fault and arc fault protection. |
| Usability | Simpler design, easy to understand and install. | More complex design with additional features. May require professional installation. |
| Cost | Generally more cost-effective. | Initial cost may be higher, but cost-effective in the long run due to reusability. |
| Maintenance | Requires replacement after each operation. | Minimal maintenance, can be reset without replacement. |
| Variety | Limited types and sizes available. | Available in various types, sizes, and with additional features for different applications. |
| Safety | May pose a risk if replaced with the wrong type. | Safer due to resettable nature and often includes safety features. |
| Environmental Impact | Some contain materials that can be hazardous. | Generally more environmentally friendly. |
While newer homes may benefit from the convenience of circuit breakers, many households still rely on traditional fuse systems. Knowing how to handle these systems, recognise when a fuse has blown, and safely replace it, remains an essential skill for homeowners in India.
Types of Fuses Commonly Used in India
With a diverse range of electrical appliances and varying electrical loads, understanding the types of fuses used in India is essential for ensuring safety and efficiency.
Different Types of Fuses and Their Relevance
Low Voltage Fuses: These are designed for household circuits and appliances
- Glass Tube Fuses: These are the most common in Indian households, typically used for small appliances. They consist of a glass cylinder with a metal wire that melts under excessive current.
- Ceramic Cartridge Fuses: Known for better heat resistance, these fuses are compact and enclosed in a ceramic body, making them suitable for higher-load applications.
- Blade Type Fuses: Primarily found in automobiles, these are also used in some low-voltage home applications.
High Voltage Fuses: Used for industrial or high-load circuits
- Expulsion Fuses: These are designed to safely release molten metal and gases during an overload, often used in industrial settings.
- Liquid-Filled Fuses: Contains a special liquid for efficient arc interruption, suitable for high-voltage applications.
- Drop-Out Fuses: Employ a mechanism where the fuse element drops out of the circuit under overload, commonly used in utility lines.
By Application:
- General Purpose Fuses: These are versatile and used for protecting basic home circuits and appliances.
- Motor Circuit Fuses: Specifically designed to handle the starting currents and overload protection of motors.
- Time Delay Fuses: These allow for brief surges in current, common in motors and air conditioners, before blowing.
- High Rupturing Capacity (HRC) Fuses: Capable of handling high short-circuit currents, these are used in more demanding applications.
By Reusability:
- One-time Use Fuses: These are the most common in Indian homes, requiring replacement after blowing.
- Rewirable Fuses: Less common due to safety concerns, these can be manually rewired with a new fuse wire.
Electrical Load in Indian Homes and Appropriate Fuse Types
| Electrical Load | Description | Appropriate Fuse Type |
| Lighting Load | Power consumed by lighting fixtures | Low-rated MCBs or fuses for lighting loads |
| Fan Load | Power consumed by ceiling fans and exhaust fans | Low-rated MCBs or fuses for fan loads |
| Appliance Load | Power consumed by household appliances | MCBs with moderate ratings or specific appliance fuses |
| Air Conditioner Load | Power consumed by air conditioning units | Higher-rated MCBs or fuses for air conditioner loads |
| Heating Load | Power consumed by geysers and heaters | MCBs or fuses suitable for heating loads |
| Power Outlet Load | Power consumed by outlets for charging and electronic devices | MCBs or fuses based on cumulative device load |
| Kitchen Appliance Load | Power consumed by kitchen appliances | MCBs or fuses suitable for kitchen appliance loads |
| Entertainment Load | Power consumed by televisions, audio systems, and gaming consoles | MCBs or fuses suitable for entertainment loads |
It's always recommended to consult with a qualified electrician for the proper selection and installation of fuses, ensuring compliance with safety standards and the unique needs of each household.
How Fuses Work?
Understanding how these small devices protect against overcurrent and overheating can be simplified by breaking down their functionality.
Here's how a fuse works:
- Metal Wire or Strip: The fuse contains a metal wire or strip, typically made of materials like copper or aluminium. This wire is chosen for its electrical conductivity.
- Protective Housing: The metal wire is housed in a protective casing, often made of glass or ceramic, to prevent external interference.
- Circuit in Normal Operation: During normal operation, when the current flowing through the circuit is within the designed limit, the metal wire remains intact.
- Excessive Current Flow: If the current flowing through the circuit exceeds a certain threshold, possibly due to a short circuit or an overload, the metal wire heats up rapidly.
- Melting of the Wire: As the current increases beyond the fuse's rated capacity, the metal wire reaches a critical temperature. At this point, the wire melts or breaks, effectively interrupting the circuit.
- Circuit Breakage: The breaking of the wire disconnects the circuit, preventing the flow of electricity. This action protects the connected devices, wiring, and overall electrical system from damage.
Common Reasons Why Fuses Blow
Fuses can blow due to various reasons, and understanding these common causes is crucial for maintaining electrical safety. Here are some typical reasons why fuses blow:
- Overloading: Connecting too many devices or appliances to a circuit can exceed the rated current capacity of the fuse. When the demand surpasses what the fuse can handle, it will blow to protect the circuit.
- Short Circuits: A short circuit occurs when a live wire comes into direct contact with a neutral or ground wire. This creates a low-resistance path, allowing a surge of current to flow, leading to the fuse blowing.
- Old or Faulty Appliances: Appliances with internal faults, damaged cords, or worn-out components can cause irregularities in the electrical flow, leading to increased current and eventual fuse failure.
- Faulty Wiring: Damaged or frayed wiring can create resistance in the circuit, causing an increase in current. This can result in the fuse blowing as it attempts to protect the circuit.
- Power Surges: Sudden spikes in voltage, often caused by lightning, faulty wiring, or issues with the power grid, can lead to an excessive current flow that exceeds the fuse's capacity.
- Loose Electrical Connections: Poorly connected wires or terminals can generate heat, increasing the resistance in the circuit. This elevated resistance may cause the fuse to blow.
- Defective Components: Faulty switches, outlets, or other electrical components can contribute to irregular current flow, triggering the fuse to blow.
- Moisture or Water Exposure: Water is a conductor of electricity, and when it comes into contact with electrical components, it can cause short circuits, leading to fuse failure.
- Improper Fuse Size: Using a fuse with a higher current rating than what the circuit requires can compromise safety. The fuse should match the circuit's specified current capacity.
- External Factors: Environmental conditions, such as extreme temperatures or corrosive atmospheres, can affect the performance of electrical components and contribute to fuse blowing.
Regular inspection of electrical systems, prompt identification, and resolution of issues, and adherence to safety guidelines can help mitigate the risk of fuse failures and ensure the reliable operation of electrical circuits.
Identifying and Handling a Blown Fuse
Encountering a blown fuse is not uncommon. Knowing how to identify and handle such situations is crucial for maintaining electrical safety. Here's a straightforward guide to help you deal with a blown fuse safely and effectively.
Identifying a Blown Fuse
1. Power Outage in Part of the Home: If you notice that power is out in only a portion of your home while the rest has electricity, it's likely due to a blown fuse.
2. Locating the Fuse Box: Most Indian homes have a fuse box located in common areas like utility rooms, garages, or sometimes near the main entrance. It's a metal box that houses the fuses.
3. Visual Inspection: Carefully open the household fuse box and look for signs of a blown fuse. Common indicators include:
- A melted, discoloured, or visibly damaged wire in a rewirable fuse.
- A cloudy or blackened appearance in a glass cartridge fuse.
- For ceramic fuses, you might not see visible damage, so you will need to test them.
4. Testing for Continuity: Using a multimeter or a continuity tester can confirm whether the fuse is blown. Ensure the power is off before testing.
Handling a Blown Fuse
1. Safety First: Before attempting to change a fuse, switch off the main power supply. Always stand on a dry surface and use insulated tools.
2. Replacing a Rewirable Fuse:
- Carefully remove the old wire.
- Cut a piece of new fuse wire of the correct rating.
- Wrap the new wire around the terminals and tighten it securely.
3. Replacing a Cartridge or Glass Fuse:
- Unscrew or pull out the blown fuse.
- Insert a new fuse of the same type and rating.
4. Post-Replacement Check: After replacing the fuse, turn on the main power supply and check if the power is restored to the previously affected area.
5. Seek Professional Help if Needed: If you're unsure about any step or if fuses blow frequently, it's best to consult a licensed electrician. Frequent blowing of fuses can indicate deeper electrical issues that require professional attention.
Maintenance Tips for Fuse-Based Electrical Systems
Here are some practical tips to help you maintain these systems effectively.
- Regular Checks: Inspect the fuse box for damage or discoloration.
- Proper Labels: Ensure circuits are labelled correctly for quick identification.
- Correct Fuse Ratings: Always use fuses with the right amperage for each circuit.
- Prompt Replacements: Replace blown fuses promptly with the same amperage.
- Consider Upgrading: Think about upgrading to circuit breakers for better protection.
- Professional Inspection: Schedule electrician inspections for overall system health.
- GFCI and AFCI: Install GFCIs in moisture-prone areas and consider AFCIs.
- Update Wiring: Update outdated wiring to meet safety standards.
- Educate Household: Ensure everyone knows the location of the fuse box and basic troubleshooting.
- Emergency Preparedness: Know the main electrical disconnect switch for emergencies.
Replacing a Fuse: A DIY Guide
Replacing a fuse is a simple task that you can safely do yourself. Here's a step-by-step guide:
Materials Needed
- Replacement fuse of the same amperage
- Fuse puller or needle-nose pliers
- Flashlight (if the fuse box is in a dark area)
Steps
- Safety First: Turn off the main power switch to ensure safety while working on the fuse box.
- Locate the Blown Fuse: Use a flashlight if needed and find the fuse that has a melted wire or discoloured appearance.
- Identify Amperage: Note the amperage written on the blown fuse. It is crucial to replace it with the same rating.
- Use Fuse Puller or Pliers: If your fuse box has a built-in puller, use it; otherwise, carefully use needle-nose pliers to grip and pull out the blown fuse.
- Insert the New Fuse: Take the new fuse and insert it into the same slot where the blown fuse was removed.
- Double-Check Orientation: Ensure the new fuse is correctly oriented and securely seated in the socket.
- Turn On Power: Turn the main power switch back on.
- Test the Circuit: Check if the circuit is functioning properly. If the new fuse blows immediately, there may be an underlying issue that requires professional attention.
- Dispose of the Blown Fuse: Safely dispose of the blown fuse.
Upgrading from Fuses to Circuit Breakers
Upgrading from traditional fuses to modern circuit breakers is a significant step towards enhancing electrical safety and efficiency in homes. Here are the benefits of such an upgrade and provide an overview of the process and costs involved, tailored for the Indian homeowner.
Benefits of Upgrading to Circuit Breakers
- Enhanced Safety: Circuit breakers provide better protection against electrical fires and shocks, a key consideration in Indian households where electrical safety standards are becoming increasingly important.
- Convenience: Unlike fuses that need to be replaced when they blow, circuit breakers can be easily reset, saving time and reducing hassle.
- Improved Power Management: Modern circuit breakers offer the ability to manage high electrical loads more efficiently, an essential factor considering the growing number of electrical appliances in Indian homes.
The Upgrade Process
- Initial Assessment: The first step is to have a qualified electrician assess your current electrical system. This assessment is crucial to determine the compatibility and requirements for the upgrade.
- Choosing the Right System: Based on the assessment, the electrician will recommend the appropriate circuit breaker panel that suits the power needs of your household.
- Installation: The process involves removing the old fuse box, installing the new circuit breaker panel, and making necessary wiring adjustments. It's essential to ensure that the installation complies with local electrical codes and standards.
Estimated Costs in India
- The cost of upgrading to circuit breakers in India varies depending on several factors, including the size of the panel, the complexity of the installation, and regional price variations.
- On average, the cost can range from ₹10,000 to ₹30,000 or more, including the panel and professional installation fees. However, these prices can vary widely based on specific home requirements and local market conditions.
Transition from Fuses to a Circuit Breaker: Trust NoBroker Electrician Services
Upgrading to a circuit breaker system from a house fuse is not a DIY project. Hire a licensed electrician for safety and compliance. Switching to circuit breakers offers enhanced safety and convenience. NoBroker Electrician Services ensures a safe transition. NoBroker Electrician Services offers reliable solutions for upgrading and maintaining electrical systems. With their professional assistance, you can seamlessly transition from older systems to modern, efficient ones. Trust us for a safer home. Contact NoBroker today.
Find Trusted Electricians Near You – City-wise
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: How does a fuse work? A fuse is a safety device that protects electrical circuits by melting when there's an overload or excessive heat, breaking the circuit to prevent damage or fires.
Ans: A fuse in a circuit is a safety device that protects against excessive currents by melting and breaking the circuit when needed, preventing electrical hazards.
Ans: Fuses are used to protect household circuits from overcurrent and overheating, preventing electrical fires and ensuring safety.
Ans: The purpose of a fuse is to protect electrical circuits from overcurrent and overheating by breaking the circuit when it detects excessive electrical flow, thereby preventing potential hazards like electrical fires in homes.
Ans: In India, you'll typically find glass tube fuses, ceramic cartridge fuses, and blade-type fuses among the most common types used to protect household electrical circuits.
Ans: An electric fuse box is a crucial component of your home's electrical system, designed to protect against overcurrent and electrical hazards by interrupting the flow of electricity when needed.
Loved what you read? Share it with others!
Most Viewed Articles

Best 10 Switch Brands in India 2026: Top Picks for Smart, Stylish, & Safe Homes
August 25, 2025
98369+ views
Top 10 Wire Companies in India: Founding Year, Valuation, Share Value and More Details in 2026
September 26, 2025
77625+ views

Wire Colour Code in India: Electrical Safety Simplified
January 31, 2025
43933+ views

10 Best Ceiling Fan Brands in India: Features, Price & Warranty in 2026
July 29, 2025
16378+ views

Installing Water Meters in Your Home Society
January 15, 2025
15557+ views
Recent blogs in
V-Guard Vs Polycab Wires: Compare Quality, Safety, Price and Durability
December 18, 2025 by Vivek Mishra
Anchor Vs Havells Wire: Copper Purity, Insulation, Durability & Safety
December 17, 2025 by Ananth
Finolex vs RR Kabel: Safety, Durability, Copper Quality and Price Range
December 17, 2025 by Vivek Mishra
Top 10 Smart Touch Switches Brands in India: Types, Price Range and Warranty
November 18, 2025 by Priyanka Saha
Types of Wiring in a House: Importance, Comparison, Costs and Safety Tips
November 18, 2025 by Priyanka Saha









 Full RM + FRM support
Full RM + FRM support
Join the conversation!