Table of Contents
Quality Service Guarantee Or Painting Free

Get a rental agreement with doorstep delivery

Find the BEST deals and get unbelievable DISCOUNTS directly from builders!

5-Star rated painters, premium paints and services at the BEST PRICES!
Loved what you read? Share it with others!
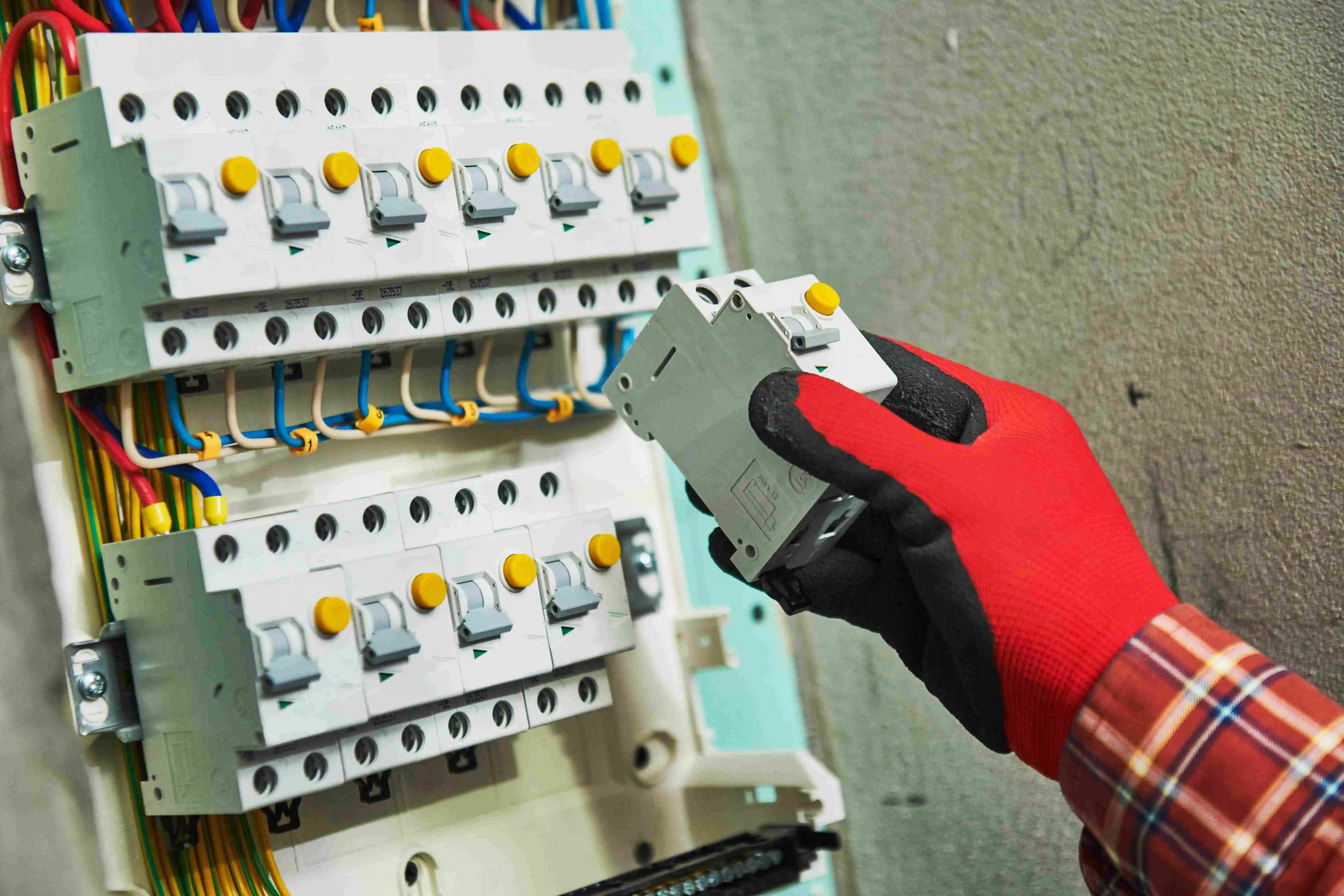

What is the Difference Between MCB, MCCB, RCB, RCD, RCCB, and RCBO: All you Need to Know
Table of Contents
Are you worried about potential electric shocks you might encounter while you're in the kitchen or the bathroom? Or do you get stressed thinking about the random fluctuations in current and how they might impact your digital gadgets? Then, having circuit breakers solves most of these problems. With circuit breakers, you can easily dodge the electrocution worries and potential appliance damage.
However, there are far too many circuit breaker types available in the market. Picking the right one for your needs requires you to learn about the difference between MCB, MCCB, RCB, RCD, RCCB and RCBO. So, keep reading this blog to learn more about them.
What are MCB and MCCB?
MCB and MCCB are circuit breakers, used in industrial settings and residential places to safeguard electrical devices by checking excessive electricity. While both MCB and MCCB are used according to specific needs, people often confuse them.
Quality Service Guarantee Or Painting Free

Get a rental agreement with doorstep delivery

Find the BEST deals and get unbelievable DISCOUNTS directly from builders!

5-Star rated painters, premium paints and services at the BEST PRICES!
MCB
The full form of MCB is a Miniature Circuit Breaker. It is an electrical circuit breaker which is used in low-current circuits to protect simple appliances from getting an overload, which could lead to overheating. This protective circuit breaker is most commonly used in home wiring. Moreover, to connect this circuit breaker, the prescribed flow of current is supposed to be between 0.5A and 125A.
MCCB
The full form of MCCB is Moulded Case Circuit Breaker. This protective barrier between high voltage and the appliances is often used with a manual switch that might be used to trip the circuit. MCCB offers an additional setting in which, other than handling excessive current, it also provides a setting for a rise in temperature. MCCB has bimetallic contacts, which, when exposed to heat, expand and contract as the temperature dips.
How are MCB and MCCB Similar?
MCB and MCCB are two different types of circuit breakers that have slightly different ways of operating when it comes to dealing with high current inflows. However, apart from menial differences, MCB and MCCB also have certain similarities, such as:
- Protect Appliances: Both MCB and MCCB have the same objective of protecting electrical appliances from excessive current and an unwanted rise in temperature.
- Operation: They both operate by automatically interrupting the current flow without the need for manual intervention or inspection.
- Safety: The circuit breakers of MCBs and MCCBs are specifically curated to safeguard electrical circuits, decreasing probable electrical risks.
- Physical Components: MCBs and MCCBs have similar components, such as a switch and a trip mechanism. Their design is almost the same.
- Appliances: MCBs and MCCBs can both be used for commercial applications, wherein the MCBs could carry less weight while the MCCBs would be able to bear more voltage.
What are the Differences between MCBs and MCCBs?
MCBs and MCCBs also bear significant differences, which can make it easier to understand their varied application and usage. Here are some of the key differences between MCB and MCCB:
| MCB | MCCB |
| These are used in low circuit currents. | They are used in heavy circuit current. |
| The tripping circuit remains fixed. | The tripping circuit is movable for MCCBs. |
| It is generally used in appliances with low energy requirements. | It is used for high energy requirements in industries. |
| They have less than 100 amps. | They can have about 2500 amps. |
| There is no manual tripping option. | There is a manual tripping option available here. |
What is RCB, RCD, RCCB, or RCBO?
RCB, RCD, RCCB and RCBO are all electric mechanisms designed to prevent electric shocks. These protect against any small current leaks by detecting such leaks and interrupting the current flow to prevent any potential hazards. Here is a detailed explanation of each of these types of electric circuit breakers:
RCB
The RCB is the most basic type of electric circuit breaker, providing protection against electrical leaks that could cause fatal shocks. The full form of RCB is a Residual Circuit Breaker. The device works by first detecting any potential current leaks and then stopping the power supply to that appliance or pathway to prevent further risks. It also measures the inflow and outflow of the current from any appliance.
RCD
RCD is another type of electric circuit breaker which has almost become similar to RCB and RCCB. The full form of RCD is Residual Current Device. This particular type of circuit is employed to detect any probable faults and leaks in the power supply inside the earth wire. This type of circuit also ensures that the current flow in phase wire and neutral wire remain in balance and an equilibrium is maintained. If the equilibrium is thrown off balance between the two wires, the RCD trips and stops the power supply to prevent risks.
RCCB
RCCB is a circuit breaker with an interesting feature that prevents people from electrocution. The full form is Residual Current Circuit Breaker. This type of circuit breaker operates by checking the balance between the current flow through the wire and the current flow back through the neutral line. If both of these pose to be balanced, then the circuit continues the current. However, if any irregularity is detected, the circuit will break. Often, this happens due to any difference in current in one line.
RCBO
RCBO is closely related to the RCCB, and the full form of RCBO is a Residual Current Breaker with Over-Current. This has a multi-functional approach, combining aspects of MCB and RCB. In fact, it not only provides protection from overcurrent but also serves as a protector against electric shocks caused by leakages and faulty wiring. RCBO is quick at detecting any leakage and breaks the circuit in that case. Moreover, in case of overloading, the thermal parts of this device trip, and the circuit breaks as well.
How are RCD and RCBO Similar?
RCD and RCBO are often found to be similar to circuit breakers protecting against potential electric leakages. They are both commonly found in fuse boxes, which are widely referred to as consumer units. RCD and RCBO also specifically safeguard against electrocution. Moreover, they both focus on reducing the chances of earth leakage faults and monitoring the equilibrium between live and neutral currents in a circuit. In case of unwanted imbalances, they trip and stop the current flow.
What is the Difference Between RCB and RCBO?
RCB and RCBO might seem like close circuit breaker cousins, but they have a lot of differences which set them apart for different uses. Here are some of the common differences between RCB and RCBO:
| RCB | RCBO |
| Primarily protects against electrical shocks. | Protects against shocks and also overcurrents. |
| Look for the imbalance between the neutral and live currents to detect risk. | It trips upon detecting excessive current to protect appliances. |
| Priority is to protect life from electrocution. | Priority is to protect appliances from overloading. |
| Stands for Residual Current Device. | Stands for Residual Current Circuit Breaker. |
| Installed in the main electrical panel in places. | Installed individually on each circuit for specific circuit-breaking options. |
What is the Difference Between RCB and MCB?
RCB and MCB are electric circuit breakers with distinct functions. Here's a table listing the differences between RCB and MCB:
| RCB | MCB |
| Provides protection against electric shock only. | Provides protection against overloading and short-circuiting. |
| It detects the imbalance in current in neutral and live lines. | It uses both magnetic and thermal tripping circuits. |
| It is used in places like bathrooms that have a higher risk of electric shocks. | It is used in residential and industrial settings. |
| Used for protecting people from electric shocks. | Used for safeguarding appliances against overloading and overheating. |
| It has two, three and four-pole options. | It has single, two, three and four-pole options. |
Electric shocks, appliance overheating, and current overloading are some of the most commonly encountered hazards. Circuit breakers, whether MCB or RCD, readily tackle these problems. They have proven to be protective systems that help prevent electrical security risks.
Additionally, if you are looking for expert electrical support, you can get in touch with NoBroker. With NoBroker's electrical services, you can install a circuit breaker effectively. Our experts are experienced and hold a 5-star rating at competitive pricing. So, reach out to us today!
Find Trusted Electricians Near You – City-wise
Frequently Asked Questions
Ans: While all of them are circuit breakers, MCB is designed to protect from overcurrent under low to medium capacity. MCCB can do the same with high current flows. Meanwhile, RCCB protects against shocks, and RCBO is a combination of both MCB and RCCB.
Ans: RCCB, also called a Residual Current Circuit Breaker, prevents electrocution and protects devices from current overloads. RCDs can only detect earth leakage currents.
Ans: MCB operates to protect against overloading and overheating. When the current overflows, a bimetallic strip in the circuit gets heated and expands, deflecting from its position, it then sets off a latch, which breaks the circuit, stopping the flow.
Ans: A fuse is an electrical gadget designed to protect against overcurrent and overloading. It is basically a metal wire or strip that melts and, hence, breaks the circuit, stopping the current flow when it encounters too much heat.
Ans: MCB is built to protect against overloading. It is divided into three categories depending on each of its capacities to take up load: type D, type C, and type B.
Loved what you read? Share it with others!
Most Viewed Articles

Best 10 Switch Brands in India 2026: Top Picks for Smart, Stylish, & Safe Homes
August 25, 2025
98052+ views
Top 10 Wire Companies in India: Founding Year, Valuation, Share Value and More Details in 2026
September 26, 2025
77392+ views

Wire Colour Code in India: Electrical Safety Simplified
January 31, 2025
43866+ views

10 Best Ceiling Fan Brands in India: Features, Price & Warranty in 2026
July 29, 2025
16285+ views

Installing Water Meters in Your Home Society
January 15, 2025
15507+ views
Recent blogs in
V-Guard Vs Polycab Wires: Compare Quality, Safety, Price and Durability
December 18, 2025 by Vivek Mishra
Anchor Vs Havells Wire: Copper Purity, Insulation, Durability & Safety
December 17, 2025 by Ananth
Finolex vs RR Kabel: Safety, Durability, Copper Quality and Price Range
December 17, 2025 by Vivek Mishra
Top 10 Smart Touch Switches Brands in India: Types, Price Range and Warranty
November 18, 2025 by Priyanka Saha
Types of Wiring in a House: Importance, Comparison, Costs and Safety Tips
November 18, 2025 by Priyanka Saha









 Full RM + FRM support
Full RM + FRM support
Join the conversation!